How Long Does Furniture Typically Last? Furniture is more than just a functional aspect of our homes and offices—it reflects our style, supports our daily activities, and creates a comfortable environment. However, like all investments, furniture has a finite lifespan, influenced by its material quality, craftsmanship, usage, and maintenance. Knowing how long different furniture pieces typically last, recognizing the signs they need replacing, and understanding ways to extend their lifespan can save you significant time and money while enhancing your space’s aesthetic and safety.
This comprehensive guide delves into the average lifespan of common furniture types, explores factors that influence durability, and provides practical tips to prolong the usability of your pieces. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to maintain your living room set, an office manager optimizing workspace furniture, or someone simply interested in maximizing their investments, this article offers valuable insights to help you make informed decisions and keep your furniture looking and functioning its best for years to come.
How Long Does Furniture Typically Last?
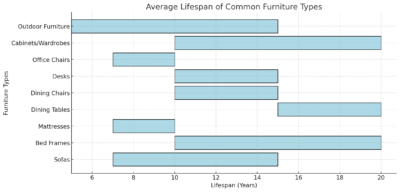
1. Sofas
- Average Lifespan: 7-15 years
- Factors Influencing Lifespan:
- Material: Leather sofas tend to last longer (10-15 years) compared to fabric ones (7-10 years).
- Frame: Hardwood frames are more durable than particleboard or softwood frames.
- Usage: Sofas in high-traffic areas wear out faster.
2. Beds and Mattresses
- Bed Frames:
- Average Lifespan: 10-20 years
- Sturdy materials like solid wood or metal can last up to 20 years, while lower-quality frames may need replacement after 5-10 years.
- Mattresses:
- Average Lifespan: 7-10 years
- Memory foam and latex mattresses last longer (10-12 years) than innerspring mattresses (5-8 years).
3. Dining Tables and Chairs
- Average Lifespan:
- Dining Tables: 15-20 years
- Dining Chairs: 10-15 years
- Durability Tips:
- Solid wood tables withstand wear better than veneer or particleboard.
- Upholstered chairs require frequent cleaning and care to maintain their appearance and structural integrity.
4. Office Furniture
- Desks:
- Average Lifespan: 10-15 years
- High-quality materials such as hardwood or steel last longer than particleboard or laminate.
- Office Chairs:
- Average Lifespan: 7-10 years
- Ergonomic office chairs with adjustable features and durable fabric extend usability.
5. Cabinets and Wardrobes
- Average Lifespan: 10-20 years
- Well-constructed cabinets with solid wood or plywood last longer compared to MDF or particleboard.
- Frequent opening and closing can affect hinges and structural integrity.
6. Outdoor Furniture
- Average Lifespan: 5-15 years
- Materials like teak, aluminum, and resin wicker withstand outdoor elements better than untreated wood or plastic.
- Proper care, such as covering furniture during harsh weather, can significantly prolong its life.
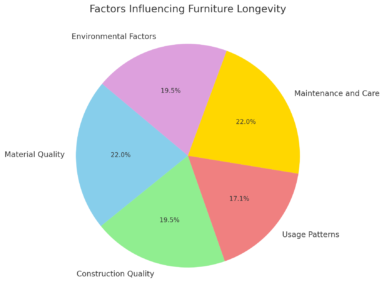
Factors Influencing Furniture Longevity
Furniture is an investment, and understanding the factors that influence its longevity can help you make more informed decisions when purchasing and maintaining it. Let’s explore these factors in detail:
1. Material Quality
The materials used in furniture play a crucial role in determining its durability and lifespan. High-quality materials such as solid wood, genuine leather, and high-grade metals are known for their longevity. For instance:
- Solid Wood: Furniture made from hardwoods like oak, maple, and teak can last decades, especially when properly maintained. In contrast, particleboard or MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) tends to wear down faster and is more prone to damage from moisture and stress.
- Leather: Genuine leather sofas or chairs can endure years of use with minimal wear, while faux leather often cracks and peels within a few years.
- Metals: High-grade metals like stainless steel or aluminum are resistant to rust and corrosion, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor furniture.
Data Insight: A study by the American Home Furnishings Alliance (AHFA) found that solid wood furniture outlasts particleboard by an average of 10-15 years.
2. Construction Quality
The craftsmanship and construction techniques used in furniture assembly significantly affect its durability. Superior joinery methods such as dovetail joints and mortise-and-tenon joints offer greater strength and longevity compared to furniture assembled with glue, nails, or staples.
- Dovetail Joints: Common in high-quality drawers, these joints resist pulling apart and provide long-lasting stability.
- Mortise-and-Tenon Joints: Used in framing and chair construction, this technique ensures a tight fit and strong bond.
On the other hand, furniture constructed using staples or glue tends to weaken over time, especially under regular use. Check for reinforcements like corner blocks in chairs or beds, which indicate better construction quality.
Tip: When buying furniture, examine the joinery and hardware for signs of quality.
3. Usage Patterns
How frequently furniture is used and the type of activities it supports can dramatically affect its wear and tear.
- High-Usage Items: Sofas, chairs, and tables in common areas like living rooms or offices are more likely to experience faster degradation due to daily use.
- Low-Usage Items: Furniture in guest rooms or decorative pieces used occasionally can maintain their condition for much longer.
Example: A sofa in a family room with children and pets will endure spills, scratches, and constant pressure, reducing its lifespan. In contrast, a similar sofa in a formal sitting room may last twice as long due to less frequent use.
Data Insight: Studies suggest that high-usage furniture such as office chairs typically lasts 7-10 years, while lightly used pieces can exceed 15 years with proper care.
4. Maintenance and Care
Regular upkeep can significantly prolong the life of your furniture. Simple habits such as cleaning, polishing, and repairing minor damages can make a difference:
- Cleaning: Dusting and vacuuming upholstered furniture prevents the buildup of dirt and allergens, which can degrade fabric over time.
- Polishing: Applying furniture polish to wooden surfaces protects against scratches and moisture damage.
- Repairs: Addressing small issues, like tightening loose screws or fixing minor cracks, prevents further deterioration.
Pro Tip: Use cleaning products that are specifically designed for the material of your furniture. For instance, leather conditioners preserve flexibility and prevent cracking, while wood oils restore natural shine.
5. Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions can greatly influence the longevity of furniture, particularly for pieces made from natural materials like wood and fabric.
- Sunlight Exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight causes fabrics to fade and wood to discolor or dry out.
- Humidity Levels: High humidity can cause wood to swell, warp, or crack, while low humidity can lead to dryness and splitting.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Extreme heat or cold can weaken adhesives and finishes, impacting furniture stability.
Prevention Tips:
- Position furniture away from windows or use UV-blocking window treatments.
- Maintain indoor humidity between 30-50% to prevent damage to wooden furniture.
- Avoid placing furniture near heat sources like radiators or fireplaces.
Data Insight: Furniture exposed to direct sunlight can lose up to 30% of its original color within one year, according to research by the Furniture Industry Research Association.
6. Manufacturing Standards
Furniture made by reputable manufacturers with strict quality control measures is likely to last longer. Companies that prioritize sustainable sourcing and precision manufacturing produce more reliable and durable pieces.
Example: Handcrafted furniture, while more expensive, often has superior longevity compared to mass-produced items.
| Factor | Impact on Longevity | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Material Quality | Solid wood and leather outlast particleboard and faux leather. | Solid oak table vs. MDF table |
| Construction Quality | Superior joinery methods extend durability. | Dovetail joints vs. glued joints |
| Usage Patterns | High-use items wear out faster than low-use items. | Office chair in daily use vs. guest chair |
| Maintenance and Care | Regular cleaning and repairs prevent deterioration. | Polishing wood table annually |
| Environmental Factors | Sunlight, humidity, and temperature cause damage. | UV fading on fabric sofa |
| Manufacturing Standards | Reputable brands ensure better quality control. | Handcrafted furniture vs. mass-produced |
Tips to Prolong Furniture Lifespan
Conclusion
Resource Links


 Related Links:
Related Links: